
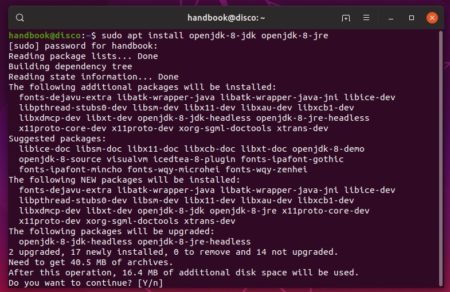
The current version as of writing this tutorial is version 8u102. This section will show you how to install Oracle Java 8. Ubuntu/Debian: sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jdkĬentOS/Fedora: sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel Ubuntu/Debian: sudo apt-get install openjdk-8-jreĬentOS/Fedora: sudo yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk The commands below will install OpenJDK 8 JRE & JDK for your distribution of choice.

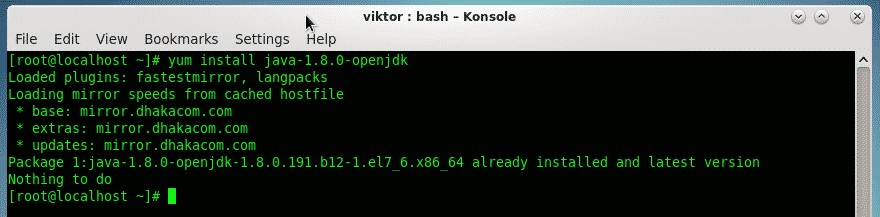
Ubuntu/Debian: sudo apt-get install openjdk-7-jdkĬentOS/Fedora: sudo yum install java-1.7.0-openjdk-devel Ubuntu/Debian: sudo apt-get install openjdk-7-jreĬentOS/Fedora: sudo yum install java-1.7.0-openjdk

The commands below will install OpenJDK 7 JRE & JDK for your distribution of choice. We will focus our installation on Java Standard Edition. Both are the same with the difference that OpenJDK is full open-source and the Oracle java has some proprietary code in it. JDK includes JRE and other software that is required for writing, developing, and compiling Java applications and applets.Īlso, there are two implementations of Java in the market, the OpenJDK and Oracle java.
JRE is an implementation of the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which allows you to run compiled Java applications and applets. There are threee variation of Java, the Standard Edition (SE), the Enterprise Edition (EE) and the Micro Edition (ME) while there are two more versions of SE that we can install, those are the Java Runtime Environment (JRE) and the Java Development Kit (JDK). This non-root account should be created from a root user account. From laptops to datacenters, game consoles to scientific supercomputers, cell phones to the Internet, Java is everywhere!īefore installing Java you should have a root or a non-root account with sudo enabled on your distribution. There are lots of applications and websites that will not work unless you have Java installed, and more are created every day. Java is a programming language and computing platform first released by Sun Microsystems in 1995.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
